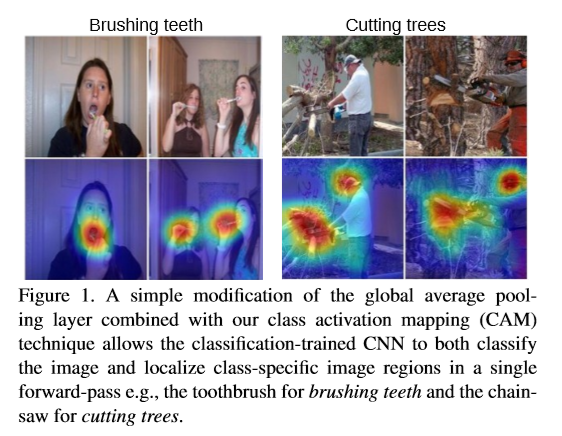
CAM 톺아보기
CAM
(Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization)
Abstract
- GAP(global average pooling)을 제안하는 논문
- Object Localization
- bounding box나 segmentation을 label로 주고 학습을 하지 않아도 이미지에서 차별적인 어떠한 영역을 localization 할 수 있다.
Introduction
Convolution layer에서는 object를 localization 할 수 있는 능력을 가지고 있지만, fully connected layers가 classification에 사용될 때 이러한 능력이 사라진다.
GoogleNet과 같은 fully convolutional network는 성능을 유지하면서 파라미터 수를 줄이기 위해 fully connected layer를 사용하지 않고 global average pooling을 사용한다.
이 논문에서는 global average pooling이 단순하게 정규화 하는 역할 뿐 아니라 약간의 조절로 네트워크는 마지막 layer까지 localization을 할 수 있는 능력을 유지 할 수 있다.
Weakly supervised object detection
기존의 supervised learning object detection은 bounding box가 정답으로 주어진 상태로 학습을 해서 위치와 class를 예측하는 학습 방법이었다면 weakly supervised object detection은 예를 들어 고양이 있는 사진 수만장을 고양이가 있다고만 알려주고 학습을 반복시키면 예측할 고양이 사진의 위치를 찾을 수 있는 학습 방법이다.
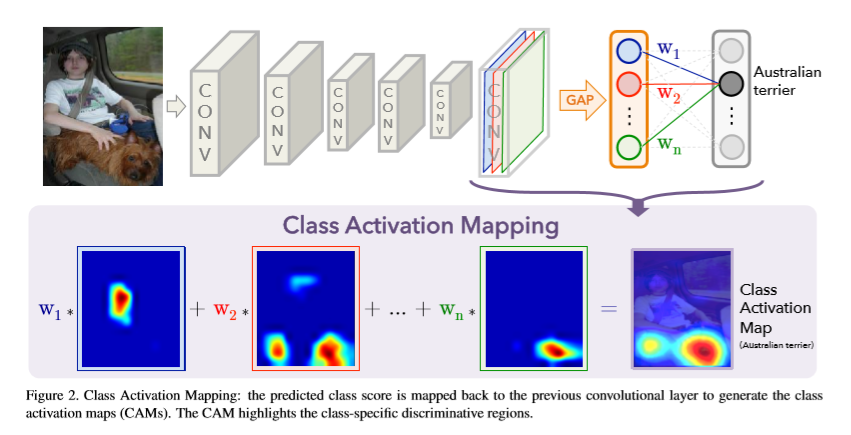
Class Activation Mapping
이 논문에서는 GoogleNet과 유사한 네트워크를 사용하고 마지막 layer 바로 전에 GAP(global average pooling)을 수행한다. 그리고 마지막 layer의 가중치를 convolution feature map에 투영시켜서 이미지의 특정 영역의 중요성을 판별할 수 있다.
위에 그림 처럼 GAP는 마지막 convolution layer에서 각 feature map의 spatial average를 출력하고 weighted sum 해서 최종적으로 class activation map을 출력하는데 사용된다.
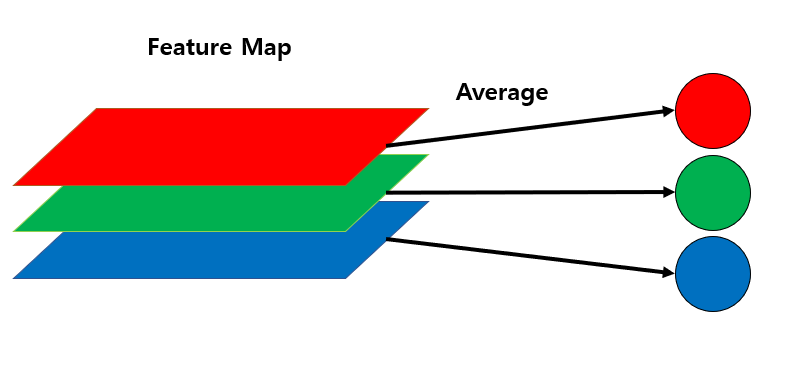
Global Average Pooling
각 feature map의 평균값을 구한다.
\(f_k(x,y)\): 마지막 convolution layer의 feature map에서 \(k\)번째 unit(channel)의 위치 \((x,y)\)의 activation을 나타낸다. 즉, 시각적인 패턴에 대한 존재를 나타내는 map이다.
\(F^k\): GAP을 수행한 결과이며 즉, \(\sum_{x,y} f_k(x,y)\)다.
\(S_c\): 주어진 class \(c\)에 대한 softmax의 input이다. 즉, \(\sum_{k} w_c^k F_k\)다.
\(w_c^k\): class \(c\)에 대한 \(F_k\)의 중요성을 나타낸다.
\(P_c\): class \(c\)에 대한 softmax의 output이다. 즉, \(\frac{exp(S_c)}{\sum_c exp(S_c)}\)
\(S_c\)를 표현해 보면
\[S_c = \sum_k w^c_k \sum_{x,y} f_k(x,y) = \sum_{x,y}\sum_k w^c_k f_k(x,y)\]그리고 class \(c\)에 대한 class activation map인 \(M_c\)을 제안한다.
\[M_c (x,y) = \sum_k w^c_k f_k(x,y)\]따라서
\[S_c = \sum_{x,y} M_c(x,y)\]즉, class activation map은 시각적인 패턴의 존재를 나타내는 \(f_k\)에 대한 weighted sum이다. 그리고 이 class activation map을 입력 이미지의 크기에 맞게 upsampling하면 특정 class와 가장 관련이 있는 영역을 시각화 할 수 있다.
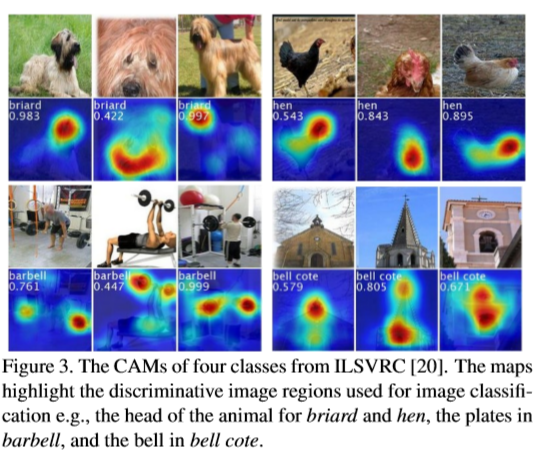
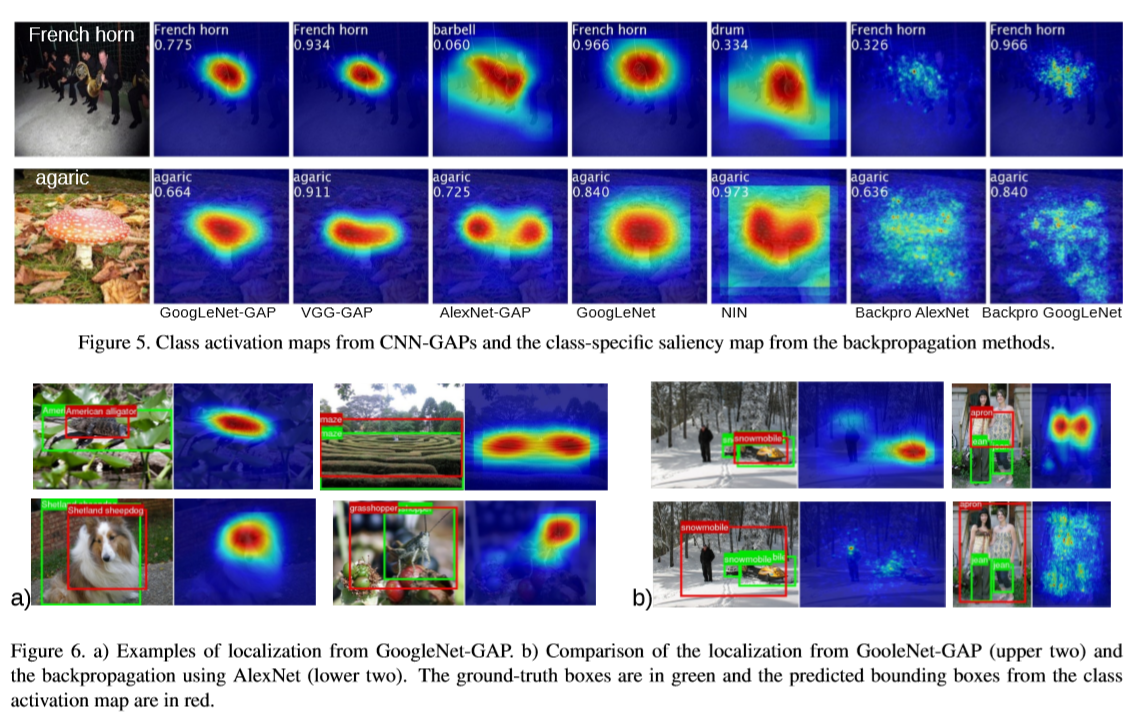
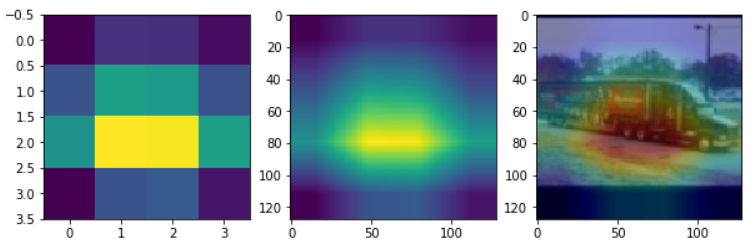
- 정량적 평가로 나타낸 CAM
Result
미리학습 시킨 모델이 있다고 가정하고 진행한다. 나는 STL10 데이터셋을 이용해서 미리 학습시켜 놓았다.
- Model : ResNet18
- Datasets : STL10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
import torch
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = 'cuda'
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.cuda.FloatTensor')
else:
device = 'cpu'
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.FloatTensor')
# STL10 class name
class_name = ['airplane', 'bird', 'car', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'horse', 'monkey', 'ship', 'truck']
# 모델 불러오기
model = ResNet18().to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('PRETRAINED_MODEL_PATH'))
model.eval()
# 마지막 feature map의 output을 가져오기 위한 hook 함수
feature_blobs = []
def hook_feature(module, input, output):
feature_blobs.append(output.cpu().data.numpy())
model._modules.get('FINAL_CONV_NAME').register_forward_hook(hook_feature)
# softmax의 input
params = list(model.parameters())
class_weights = np.squeeze(params[-2].cpu().data.numpy())
# 이미지 불러오기
img_path = 'TEST_IMG_PATH'
img = Image.open(img_path)
# 테스트 할 이미지 변환하기(resize, tensor)
cvt_tensor = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((128,128)),
transforms.ToTensor()])
tensor_img = cvt_tensor(img).to(device)
tensor_img = tensor_img.view(1, 3, 128,128)
# 예측하기
output = model(tensor_img)
h_x = F.softmax(output, dim=1).data.squeeze()
pred = h_x.argmax(0).item()
# CAM 계산하기
final_conv = feature_blobs[0][0]
cam = np.zeros(dtype=np.float32, shape=final_conv.shape[1:3])
for i, w in enumerate(class_weights[pred]):
cam += w*final_conv[i,:,:]
# scaling
cam = cam - np.min(cam)
cam = cam / np.max(cam)
CAM을 계산하는 과정을 거친뒤 Heatmap을 출력한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 출력하기
import cv2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10,10))
axs[0].imshow(cam)
resized_cam = cv2.resize(cam, (128, 128))
axs[1].imshow(resized_cam)
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(np.uint8(255 * resized_cam), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.resize(img, (128,128))
heatimg = heatmap*0.3 + img*0.5
cv2.imwrite('./cam.jpg', heatimg)
cam_img = cv2.imread('./cam.jpg')
cam_img = cv2.cvtColor(cam_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
axs[2].imshow(cam_img)