Deep Sort 톺아보기
논문의 번역과 이해가 내가 느끼기엔 어렵고 복잡하기 때문에 소스코드를 분석해서 이해해보는 것이 나을거 같다.
- PAPER
- cosine metric learning : GitHub
- deep sort : GitHub
- 번역한 GitHub
이 포스트는 GitHub를 리뷰한 포스트 입니다.
DataSet
MARS와 MARKET 2개가 있었지만 MARS는 다운로드가 잘안되서.. MARKET으로만 하겠습니다.
실행
깃허브의 소스코드를 clone하면 간단하게 실행을 시켜볼 수 있다. 이건 간략하게 실행 부분만 가져온 것이고 자세하게 설치/실행하는 방법은 위에 깃허브의 Read.md를 읽어봐야한다.
학습
1
2
3
4
5
python train_market1501.py \
--dataset_dir=./Market-1501-v15.09.15/ \
--loss_mode=cosine-softmax \
--log_dir=./output/market1501/ \
--run_id=cosine-softmax
추적
1
python deep_sort_app.py --sequence_dir=./MOT16/test/MOT16-06 --detection_file=./resources/detections/MOT16_POI_test/MOT16-06.npy --min_confidence=0.3 --nn_budget=100 --display=True
개념
일단 코드를 살펴보기전에 Euclidean,Cosine Distance의 개념에 대해서 알고가야 매우 쉽게 할수 있다.
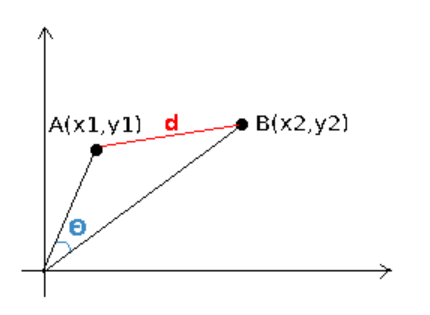
Euclidean
우리가 눈으로 보며 줄자를 이용해 거리를 측정하는 것과 유사하다.
Cosine Distance
코사인 유사도는 무게와 크기는 고려하지않고 벡터사이의 각도만으로 측정한다.
코드
전부다 까면 오래 걸리고 사용할 수 있는 방법을 알아보기 위해 실질적이게 사용하는 부분과 간단한 개념만 볼것이다.
main
1
2
3
4
5
6
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
run(
args.sequence_dir, args.detection_file, args.output_file,
args.min_confidence, args.nms_max_overlap, args.min_detection_height,
args.max_cosine_distance, args.nn_budget, args.display)
run
이게 실질적으로 동작하는 예제 코드다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
def run(sequence_dir, detection_file, output_file, min_confidence,
nms_max_overlap, min_detection_height, max_cosine_distance,
nn_budget, display):
"""
multi-target tracker 실행
Parameters
----------
sequence_dir : str
시퀀스 데이터 경로
detection_file : str
검출 파일
output_file : str
output file 경로 / 추적 결과를 포함
min_confidence : float
confidence 임계값 / 이보다 낮은 confidence는 무시하게 된다.
nms_max_overlap: float
Maximum detection overlap (NMS 임계값)
min_detection_height : int
height 임계값 / 이보다 낮은 height는 무시하게 된다.
max_cosine_distance : float
cosine distance metric 임계값
nn_budget : Optional[int]
Maximum size of the appearance descriptor gallery. If None, no budget is enforced.
display : bool
True : 시각화
"""
# 시퀀스 정보수
seq_info = gather_sequence_info(sequence_dir, detection_file)
# cosine distance metric 사용
metric = nn_matching.NearestNeighborDistanceMetric(
"cosine", max_cosine_distance, nn_budget)
tracker = Tracker(metric)
results = []
# 프레임 마다 호출
def frame_callback(vis, frame_idx):
print("Processing frame %05d" % frame_idx)
# detection 생성
detections = create_detections(
seq_info["detections"], frame_idx, min_detection_height)
detections = [d for d in detections if d.confidence >= min_confidence]
# NMS 실행
boxes = np.array([d.tlwh for d in detections])
scores = np.array([d.confidence for d in detections])
indices = preprocessing.non_max_suppression(
boxes, nms_max_overlap, scores)
detections = [detections[i] for i in indices]
# tracker 업데이트 이 부분에서 detection을 업데이트 해서 객체를 추적한다.
# 내가 내 코드에 결합하고 싶을 때 사용하는 방법을 이해하기 위해 포스트를 작성했기 떄문에
# 자세하게 보고싶으면 SORT 포스트를 보자 비슷한거 같다.
tracker.predict()
tracker.update(detections)
# 시각화
if display:
image = cv2.imread(
seq_info["image_filenames"][frame_idx], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
vis.set_image(image.copy())
vis.draw_detections(detections)
vis.draw_trackers(tracker.tracks)
# 결과를 저장한다.
for track in tracker.tracks:
if not track.is_confirmed() or track.time_since_update > 1:
continue
bbox = track.to_tlwh()
results.append([
frame_idx, track.track_id, bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[2], bbox[3]])
# 객체를 추적하는 시작부분 frame_callback을 매 프레임 호출한다.
if display:
visualizer = visualization.Visualization(seq_info, update_ms=5)
else:
visualizer = visualization.NoVisualization(seq_info)
visualizer.run(frame_callback)
# 결과를 저장한다.
f = open(output_file, 'w')
for row in results:
print('%d,%d,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,1,-1,-1,-1' % (
row[0], row[1], row[2], row[3], row[4], row[5]),file=f)
gather_sequence_info
시퀀스의 정보를 수집한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
def gather_sequence_info(sequence_dir, detection_file):
"""
시퀀스의 정보를 수집하는 함수
Parameters
----------
sequence_dir : str
MOTChallenge sequence directory 경로
detection_file : str
detection file 경로
Returns
-------
디렉토리의 시퀀스 정보:
* sequence_name: 시퀀스 이름
* image_filenames: 파일 이름
* detections: MOTChallenge 형식의 검출 파일
* groundtruth: MOTChallenge 형식의 groud-truth
* image_size: Image size (height, width).
* min_frame_idx: 첫번째 인덱스의 이름
* max_frame_idx: 마지막 인덱스의 이름
"""
# 이미지 경로
image_dir = os.path.join(sequence_dir, "img1")
# 파일이름
image_filenames = {
int(os.path.splitext(f)[0]): os.path.join(image_dir, f)
for f in os.listdir(image_dir)}
# 실제값
groundtruth_file = os.path.join(sequence_dir, "gt/gt.txt")
detections = None
# 검출 파일 불러오기
if detection_file is not None:
detections = np.load(detection_file)
groundtruth = None
# 실제값 불러오기
if os.path.exists(groundtruth_file):
groundtruth = np.loadtxt(groundtruth_file, delimiter=',')
# 시퀀스 이미지 읽기
if len(image_filenames) > 0:
image = cv2.imread(next(iter(image_filenames.values())),
cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
image_size = image.shape
else:
image_size = None
# index
if len(image_filenames) > 0:
min_frame_idx = min(image_filenames.keys())
max_frame_idx = max(image_filenames.keys())
else:
min_frame_idx = int(detections[:, 0].min())
max_frame_idx = int(detections[:, 0].max())
# 시퀀스 정보
info_filename = os.path.join(sequence_dir, "seqinfo.ini")
if os.path.exists(info_filename):
with open(info_filename, "r") as f:
line_splits = [l.split('=') for l in f.read().splitlines()[1:]]
info_dict = dict(
s for s in line_splits if isinstance(s, list) and len(s) == 2)
update_ms = 1000 / int(info_dict["frameRate"])
else:
update_ms = None
feature_dim = detections.shape[1] - 10 if detections is not None else 0
seq_info = {
"sequence_name": os.path.basename(sequence_dir),
"image_filenames": image_filenames,
"detections": detections,
"groundtruth": groundtruth,
"image_size": image_size,
"min_frame_idx": min_frame_idx,
"max_frame_idx": max_frame_idx,
"feature_dim": feature_dim,
"update_ms": update_ms
}
return seq_info
cosine_distance
cosine distance를 이용해 반환을 하는 부분이다. deep sort는 cosine distance를 기준으로 만들어졌기에 cosine distance기준으로 본다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
def _cosine_distance(a, b, data_is_normalized=False):
if not data_is_normalized:
a = np.asarray(a) / np.linalg.norm(a, axis=1, keepdims=True)
b = np.asarray(b) / np.linalg.norm(b, axis=1, keepdims=True)
return 1. - np.dot(a, b.T)
def _nn_cosine_distance(x, y):
distances = _cosine_distance(x, y)
return distances.min(axis=0)
class NearestNeighborDistanceMetric(object):
"""
각 target에 대해 지금까지 관측된 샘플에 가장 가까운
거리를 반환하는 nearest neighbor distance metric
Parameters
----------
metric : "euclidean" , "cosine".
matching_threshold: 일치하는 임계값 / 거리가 더 크면 잘못된 것으로 탐지
budget : class당 샘플을 budget 이하로 수정 / 가장 오래된 샘플을 제거
Attributes
----------
samples : Dict[int -> List[ndarray]]
target id에서 지금까지 관찰된 샘플 목록으로 매핑
"""
def __init__(self, metric, matching_threshold, budget=None):
if metric == "euclidean":
self._metric = _nn_euclidean_distance
elif metric == "cosine":
self._metric = _nn_cosine_distance
else:
raise ValueError(
"Invalid metric; must be either 'euclidean' or 'cosine'")
self.matching_threshold = matching_threshold
self.budget = budget
self.samples = {}
def partial_fit(self, features, targets, active_targets):
"""Update the distance metric with new data.
Parameters
----------
features : ndarray
An NxM matrix of N features of dimensionality M.
targets : ndarray
An integer array of associated target identities.
active_targets : List[int]
A list of targets that are currently present in the scene.
"""
for feature, target in zip(features, targets):
self.samples.setdefault(target, []).append(feature)
if self.budget is not None:
self.samples[target] = self.samples[target][-self.budget:]
self.samples = {k: self.samples[k] for k in active_targets}
def distance(self, features, targets):
"""Compute distance between features and targets.
Parameters
----------
features : ndarray
An NxM matrix of N features of dimensionality M.
targets : List[int]
A list of targets to match the given `features` against.
Returns
-------
ndarray
Returns a cost matrix of shape len(targets), len(features), where
element (i, j) contains the closest squared distance between
`targets[i]` and `features[j]`.
"""
cost_matrix = np.zeros((len(targets), len(features)))
for i, target in enumerate(targets):
cost_matrix[i, :] = self._metric(self.samples[target], features)
return cost_matrix
deep sort에서는 객체의 위치와 그 다음 프레임에서 객체의 위치를 찾기 위해 cosine similarity를 사용하는 것으로 추정된다. 엄청난 수식이지만 일단 풀어보진 않고 이렇다만 알아두고 넘어가야 할거 같다..
create_detections
detection 파일을 이용해 주어진 프레임에 대해서 detectio list를 만든다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
def create_detections(detection_mat, frame_idx, min_height=0):
"""
주어진 프레임에 대한 detection을 만들기
Parameters
----------
detection_mat : ndarray
detection matric은 처음 10개 열은 MOTChallenge 형식이고
나머지 열은 각 detection과 연관된 벡터가 저장된다.
frame_idx : int
프레임 인덱스
min_height : Optional[int]
최소 bounding box 높이 / 이것보다 작으면 무시한다.
Returns
-------
List[tracker.Detection]
detection 반환
"""
frame_indices = detection_mat[:, 0].astype(np.int)
mask = frame_indices == frame_idx
detection_list = []
# detection parsing
for row in detection_mat[mask]:
bbox, confidence, feature = row[2:6], row[6], row[10:]
if bbox[3] < min_height:
continue
detection_list.append(Detection(bbox, confidence, feature))
return detection_list
NMS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
def non_max_suppression(boxes, max_bbox_overlap, scores=None):
"""
Parameters
----------
boxes : ndarray
ROI 배열 (x, y, width, height).
max_bbox_overlap : float
이 값보다 겹치는 ROI는 억제된다.
scores : Optional[array_like]
confidence 점수
Returns
-------
List[int]
NMS 반환
"""
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
boxes = boxes.astype(np.float)
pick = []
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2] + boxes[:, 0]
y2 = boxes[:, 3] + boxes[:, 1]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
if scores is not None:
idxs = np.argsort(scores)
else:
idxs = np.argsort(y2)
while len(idxs) > 0:
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
overlap = (w * h) / area[idxs[:last]]
idxs = np.delete(
idxs, np.concatenate(
([last], np.where(overlap > max_bbox_overlap)[0])))
return pick